Chest Wall Pain: Symptoms, Treatment and Relief Options
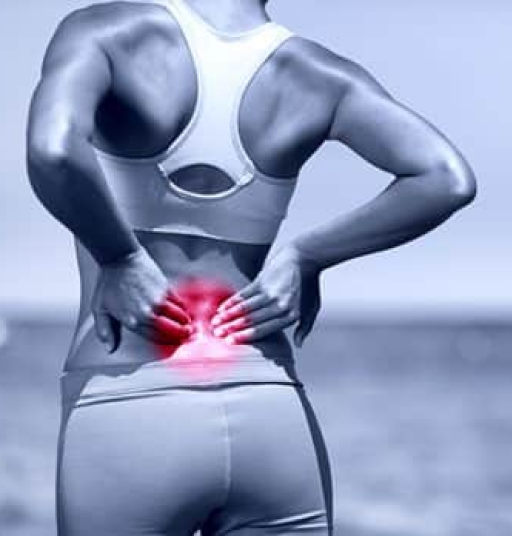
Chest wall pain is a common experience that many people encounter throughout their lives. It's a type of discomfort that can range from a dull ache to a sharp sting in the area between your neck and abdomen.
While it might be easy to assume that all chest discomfort is heart-related, the reality is far from it. The anatomy of the chest is complicated and houses more than just your heart — there are muscles, bones, joints, and tissues, all of which can be sources of discomfort.
Understanding the different types of chest pain is essential for your peace of mind and health. It can help you identify when a trip to a healthcare professional is necessary or when the discomfort can be managed with lifestyle adjustments.
What Is the Chest Wall?
The chest wall is an intricate structure that protects some of the body's most vital organs, including the heart and lungs. It comprises the rib cage, intercostal muscles, the sternum or breastbone, and the costochondral joints, which connect your ribs to your sternum. The chest wall also includes the soft tissue surrounding these structures.
What exactly does this wall do? Its primary function is to support breathing mechanics and protect the organs within. However, the chest wall isn't immune to discomfort. It can experience strains, stress fractures, and other conditions that can lead to discomfort.
What Is Chest Wall Pain?
Chest wall pain, also known as musculoskeletal chest wall pain, is a term that encompasses any discomfort originating from structures in the chest wall, including the ribs, sternum, and chest muscles. Various conditions can lead to chest wall pain, such as costochondritis, known as inflammation of the cartilage in the rib cage, or Tietze syndrome, a rare condition causing swelling in the upper ribs.
It's important to distinguish between non-cardiac chest pain and heart-related chest pain. Non-cardiac chest pain, such as that caused by fibromyalgia or a muscle strain, might feel similar to a heart condition, like angina.
However, they stem from different causes and require different treatment approaches. Heart-related chest pain is often associated with life-threatening conditions such as heart disease or a heart attack, and it requires immediate medical attention.
Non-cardiac chest pain, while potentially severe, is typically not life-threatening. Regardless of the type, a healthcare professional should evaluate any persistent chest discomfort to determine the cause and appropriate treatment options.
What Are Common Causes of Chest Wall Pain?
Different conditions can lead to chest wall pain, each with unique characteristics and treatment approaches.
Costochondritis is one of the more common culprits. It's a condition that involves swelling of the costochondral junctions, where the upper ribs join with the cartilage that holds them to the breastbone. Deep breathing or physical activity can cause localized chest wall pain that often worsens.
Tietze syndrome, while less common, is another cause of chest wall pain. This condition is similar to costochondritis but differs because it usually involves swelling of the costochondral joints. Tietze syndrome typically affects the second and third ribs, and the discomfort can sometimes radiate to the arms and shoulders.
Fibromyalgia is a long-term condition that causes pain all over the body, including the chest wall. People with fibromyalgia often experience tenderness in the chest area, which can mimic the symptoms of chest wall pain.
Musculoskeletal chest wall pain can occur due to various conditions that affect the chest wall's muscles, bones, and joints. These can include rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting many joints, including the hands and feet, and ankylosing spondylitis, a type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine.
Injury to the chest wall, such as rib fractures or stress fractures, can also result in chest wall pain. These injuries can occur due to trauma, such as a fall or direct blow to the chest, or due to overuse, such as from intense or repetitive physical activity.
Sometimes, even everyday activities can cause discomfort in the chest wall. Physical activities that involve the chest muscles, such as weightlifting or even intense coughing, can sometimes contribute to discomfort in the chest wall.
What Are the Symptoms of Chest Wall Pain?
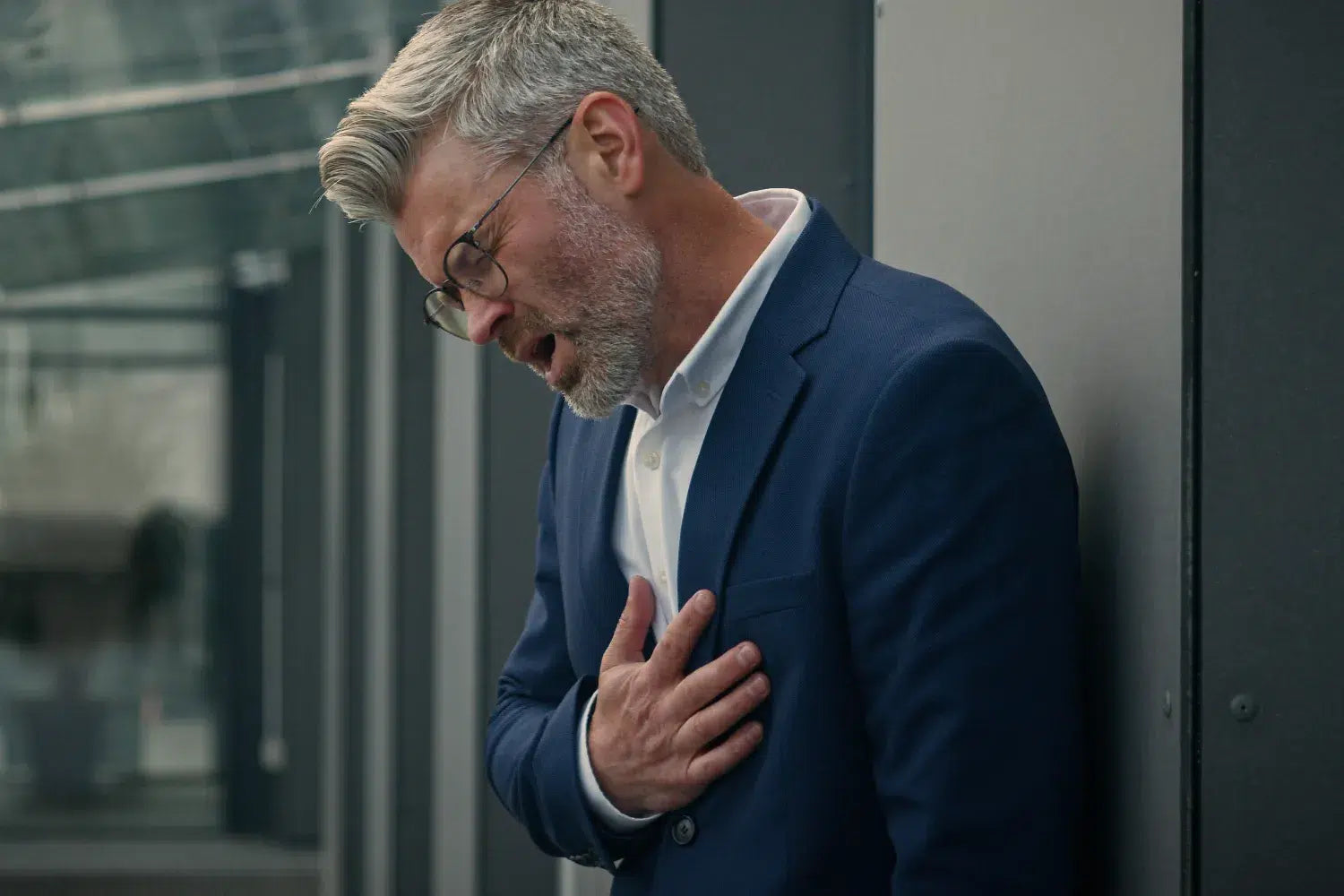
Recognizing the symptoms of chest wall pain can help you understand when it's time to seek help. The discomfort associated with chest wall pain can vary greatly from person to person, but there are some common signs to look out for.
Sharp pain is a typical symptom of chest wall pain. This pain is often localized, confined to one area, like the sternum or rib cage. The pain might also worsen with deep breathing, as breathing involves the movement of the chest wall, which can aggravate the discomfort if there's an issue with the structures in the chest wall.
Shortness of breath can accompany chest wall pain, especially if the pain is severe or sudden. If you're experiencing this symptom, seeking medical attention promptly is necessary.
Chest wall pain can also manifest as severe pain in the anterior area of the chest, which is the front part of the chest.
It's important to remember that non-cardiac chest pain can feel similar to the pain associated with heart conditions. If you're experiencing persistent chest discomfort, getting it checked out by a healthcare professional is always a good idea.
How Is Chest Wall Pain Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of chest wall pain often begins with a detailed medical history. This helps healthcare professionals identify underlying conditions or activities contributing to the discomfort. It's important to provide as much information as possible about the nature of the pain, such as when it started, what makes it better or worse, and any associated symptoms.
Diagnostic tests, like a chest x-ray, can help rule out other causes of chest pain, such as heart conditions or lung diseases. In some cases, a physical examination may be sufficient to diagnose conditions affecting the costochondral junctions or identify symptoms of costosternal syndrome.
What Are the Treatment Options for Chest Wall Pain?
There are several ways to manage chest wall pain — the best approach often depends on the underlying cause.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help reduce discomfort and inflammation in the chest wall. Healthcare professionals might sometimes recommend corticosteroids to help manage severe inflammation.
Physical therapy can be beneficial, especially for conditions like costochondritis or Tietze syndrome. It involves exercises and stretches that help improve flexibility, reduce discomfort, and support healing in the chest wall.
Heat and cold compresses can offer temporary relief for affected areas. Warmth can help loosen tight muscles, while cold can help numb the area and reduce inflammation.
It's important to seek medical care if you're experiencing chest wall pain. While it's often not life-threatening, chest wall pain can sometimes indicate serious conditions.
If the discomfort is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms like shortness of breath or chest tightness, it's important to seek immediate medical attention. Emergency room visits are necessary for life-threatening conditions like a heart attack, angina, or pulmonary embolism.
What Are Tips for Managing Chest Wall Discomfort?
Living with chest wall pain can be challenging, but certain lifestyle adjustments can help manage the discomfort and improve your quality of life. Regular physical activity, when done correctly and under the guidance of a healthcare professional, can help strengthen your chest wall and reduce discomfort. Good posture can also make a significant difference, as it helps keep your chest wall structures aligned and minimizes strain.
Stress can also affect the chest wall, causing muscle tension and discomfort. Finding effective stress management methods, like practicing mindfulness or meditation, can relieve stress.
It's important to understand your condition and how it impacts your life. This understanding can help you make informed decisions about your lifestyle and treatment options. Regular check-ins with healthcare professionals are essential as they can monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Can CBD Help With Chest Wall Discomfort?
CBD, or cannabidiol, is a natural compound found in cannabis plants. It works with your body's endocannabinoid system (ECS), which plays a role in maintaining balance throughout your body, including levels of stress and discomfort.
The ECS has CB receptors throughout the brain and body. CBD can subtly interact with these receptors, supporting healthy stress levels and potentially helping to ease feelings of discomfort. This interaction can help manage chest wall discomfort in some cases.
CBD oils and gummies can support full-body balance and the body's response to stress as they are absorbed into the bloodstream. Topical forms of CBD, like our CBD Balms, provide targeted support and can be applied directly to the chest wall. They interact with the local CB receptors to temporarily ease minor feelings of discomfort as needed.
While CBD can support overall balance and potentially help ease feelings of stress and discomfort, it is not a cure-all. If chest wall discomfort indicates an underlying issue, more comprehensive treatment may be needed.
The Bottom Line
Understanding chest wall pain — its causes, symptoms, and treatment options — is key to managing this common condition. Listening to your body and seeking medical advice if you're experiencing chest discomfort is imperative. Remember, your health and well-being are worth prioritizing.
At Muscle MX, we’re here to help elevate your wellness routine. Check out our natural, third-party tested CBD products designed to work with your body's natural systems to help ease minor feelings of discomfort and support your body in adapting to everyday stressors.
Sources:
The Anatomy of the Ribs and the Sternum and Their Relationship to Chest Wall Structure and Function | ScienceDirect
Musculoskeletal chest wall pain | RACGP
Ice Packs vs. Warm Compresses For Pain | Johns Hopkins Medicine
Guide to Good Posture | MedlinePlus
Enhancing Endocannabinoid Control of Stress with Cannabidiol | PMC