THCA vs THC: The Real Difference Explained
Key Takeaways
Understanding the fundamental differences between THCA and THC empowers you to make informed decisions about cannabis consumption and maximize therapeutic benefits while managing psychoactive effects.
-
THCA doesn't get you high - Raw THCA lacks psychoactive effects due to its larger molecular structure that prevents CB1 receptor binding in your brain.
-
Heat transforms THCA into THC - Decarboxylation at 220-250°F converts 87.7% of THCA to psychoactive THC, explaining why smoking produces effects but raw consumption doesn't.
-
Different therapeutic profiles - THCA offers anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective benefits without intoxication, while THC provides pain relief comparable to codeine plus appetite stimulation.
-
Consumption method determines effects - Raw cannabis juicing preserves THCA benefits (500-600mg tolerable), while smoking/vaping activates THC (10-25mg typical threshold).
-
Legal status creates gray areas - THCA exists in federal legal limbo as hemp-derived products, but converts to controlled THC when heated, creating complex state-by-state regulations.
This knowledge allows you to choose between non-intoxicating therapeutic benefits through raw THCA consumption or the full spectrum of effects through heated THC activation, depending on your specific wellness goals and legal considerations.
Introduction
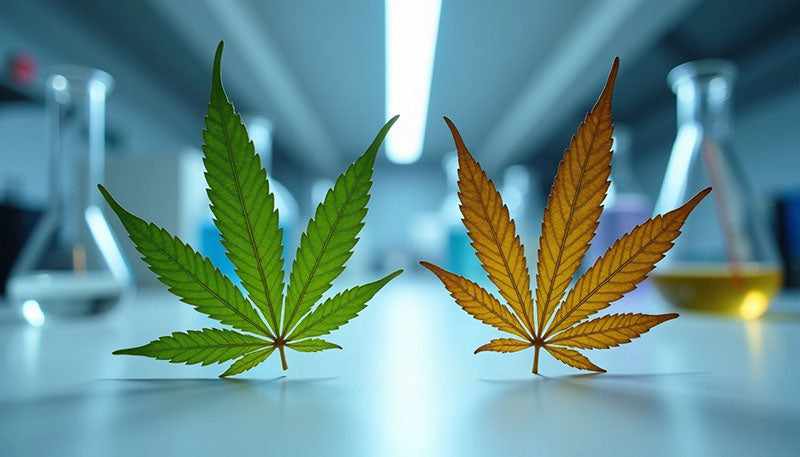
THCA vs THC — at first glance, you might think it's just a simple one-letter difference, but these compounds are as different as night and day when it comes to how they affect your body. The cannabis plant contains somewhere between 80 to 100 different cannabinoids, and while THC has earned its reputation for psychoactive effects, THCA tells a completely different story.
What sets these compounds apart? The answer lies in their chemical makeup and how they interact with your body's systems. THCA stays non-intoxicating in its raw state because of its larger molecular structure, which can't properly fit into the specific receptors in your brain. But here's where it gets interesting — when you apply heat through a process called decarboxylation, THCA transforms into THC. This explains why munching on raw cannabis leaves won't produce any psychoactive effects, while smoking or vaping the same plant definitely will.
"Does THCA get you high?" — it's one of the most common questions we hear, and the answer is straightforward: no, not in its raw form. Heat is the key that unlocks THC's psychoactive potential. Yet both compounds bring their own therapeutic benefits to the table. THCA shows promise for its anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective qualities, while THC can provide pain relief that rivals codeine but without the harsh side effects.
Let's explore what makes these cannabinoids unique and how they might support your wellness goals. Whether you're curious about their medical potential or wondering which one packs more potency, we're here to guide you through the science and help you make informed choices.
Chemical Structure and Conversion Process
Understanding the molecular makeup of THCA and THC reveals exactly why these cannabinoids behave so differently in your body. The structural differences between these compounds determine everything from their therapeutic potential to their psychoactive effects.
Molecular Difference: THCA's Carboxyl Group vs THC
The key distinction comes down to one crucial component: THCA contains an extra carboxyl group (-COOH) that THC lacks. This might sound like a minor detail, but it changes everything about how these compounds work. THCA (C₂₂H₃₀O₄) is simply too large compared to THC (C₂₁H₃₀O₂), making it impossible to fit properly into the cannabinoid receptors in your brain. Think of it like trying to fit a square peg into a round hole — the shape just doesn't match up, which is why raw cannabis containing THCA won't produce any psychoactive effects.
Decarboxylation: How THCA Becomes THC
The transformation from THCA to THC happens through a process called decarboxylation — essentially a chemical reaction that strips away the carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide. This process occurs naturally over time when exposed to light or air, but it's incredibly slow. Heat, however, speeds things up dramatically.
Research shows that heating THCA between 220°F and 250°F (104°C-121°C) for 30-45 minutes creates the most efficient conversion. Higher temperatures work even faster — complete conversion happens in just 30 minutes at 110°C, 9 minutes at 130°C, and only 6 minutes at 145°C. This explains why smoking or vaping cannabis works so quickly — those high temperatures instantly convert THCA into active THC.
Is THCA the Same as THC?
While they're closely related, THCA and THC are distinctly different compounds. THCA acts as THC's precursor in the cannabis plant. That carboxyl group we mentioned earlier prevents THCA from binding effectively to CB1 receptors in your brain.
Here's something interesting: decarboxylation doesn't always convert 100% of THCA. Studies have found THCA in urine and blood samples from cannabis users, with concentrations reaching up to 10.8 ng/mL in urine and 14.8 ng/mL in blood serum. Even more intriguing, THCA actually binds to and activates PPARγ receptors more effectively than THC does, suggesting it has unique therapeutic potential beyond just being THC's starting point.
What Are the Psychoactive Effects and Potency Differences?
The psychoactive experience you get from cannabis comes down to one key factor — which cannabinoid is calling the shots, THCA or THC. Understanding how these compounds affect your body differently helps explain why some cannabis products leave you feeling intoxicated while others don't.
Does THCA Get You High?
The answer is clear-cut: no. THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) doesn't produce psychoactive effects in its raw form. This happens because THCA simply can't bind to the CB1 receptors in your brain. Think of it like trying to fit a square peg into a round hole — the molecular structure just doesn't match up.
When you heat cannabis through smoking, vaping, or cooking, THCA transforms into THC, and that's when psychoactive effects become possible. This is why eating raw cannabis rich in THCA won't create that characteristic "high" you might expect from marijuana use.
THCA vs THC: Which Packs More Punch?
When it comes to psychoactive strength, THC wins hands down because it directly activates those CB1 receptors. THCA brings therapeutic benefits to the table, but it lacks THC's intoxicating power.
Here's something interesting to keep in mind: roughly 87.7% of THCA converts to THC during the heating process. So if you see a flower labeled as containing 30% THCA, you're looking at approximately 26.3% usable THC after decarboxylation.
How THC Changes Your Perception
THC's psychoactive effects come from its ability to latch onto CB1 receptors scattered throughout your brain's cerebellum, hippocampus, and cortex. Once attached, it triggers changes in how neurotransmitters are released, which affects everything from memory processing to mood regulation and motor control.
Ever notice how time seems to crawl when you're under the influence? THC can distort your perception of time, making minutes feel like hours, while also heightening your sensory experiences. Remember, frequent cannabis users often find these effects become less pronounced over time as tolerance builds.
What Are the Therapeutic Benefits and Medical Uses?
The medical applications of THCA and THC extend far beyond their structural differences. Each compound offers unique therapeutic benefits that make them valuable for different health concerns and patient needs.
THCA's Anti-inflammatory and Neuroprotective Properties
THCA demonstrates significant anti-inflammatory potential through its ability to inhibit cyclooxygenase enzymes COX-1 and COX-2. Research suggests it may provide relief for conditions like arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. What makes this particularly interesting is that THCA reduced arthritis symptoms in mice while preventing inflammatory cell infiltration and protecting cartilage from damage.
The neuroprotective qualities of THCA are equally promising. Scientists have found it may help shield brain cells from damage, potentially supporting those dealing with neurodegenerative disorders such as Huntington's disease. Additional studies show THCA can lower Aβ and p-tau levels, which are key markers in Alzheimer's disease research.
THC for Pain, Appetite, and Nausea Management
When it comes to pain management, THC provides pain relief comparable to codeine. Research shows THC works particularly well for cancer-related pain and neuropathic pain. THC also stimulates appetite by triggering the release of ghrelin, commonly known as the "hunger hormone".
Cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy often turn to THC for nausea and vomiting control. One study revealed that combining cannabis with standard anti-nausea medications achieved a 24% complete response rate compared to just 8% with standard medications alone.
Medical Use: The Key Difference Between THC and THCA
The most important distinction in medical applications comes down to psychoactivity. THCA delivers therapeutic benefits without any intoxicating effects, making it an ideal choice for patients who need to maintain clear thinking and cognitive function. THC, while medically beneficial, comes with psychoactive effects that may not be suitable for all patients or medical situations.
Understanding this difference helps patients and healthcare providers choose the most appropriate cannabinoid for specific medical needs and lifestyle requirements.
Consumption Methods and Legal Status
Your consumption method makes all the difference in whether you experience THCA's gentle therapeutic effects or THC's more pronounced psychoactive properties. Understanding these differences can help you make informed choices that align with your wellness goals and legal considerations.
Raw vs Heated: Juicing, Smoking, and Edibles
Want to experience THCA without any psychoactive effects? Raw consumption through juicing or smoothies keeps THCA in its original form. On the flip side, smoking, vaping, or cooking cannabis triggers decarboxylation, transforming THCA into THC. Most edibles you'll find at dispensaries contain THC since manufacturers apply heat during production.
Here's something interesting — raw cannabis juicing allows you to consume 500-600mg of THCA, which far surpasses the 10-25mg THC threshold that most people can comfortably handle. This opens up possibilities for those seeking therapeutic benefits without intoxication.
Legal Loopholes: Why THCA Is Federally Legal
The 2018 Farm Bill created an interesting legal landscape. Hemp-derived products containing less than 0.3% delta-9 THC remain federally legal. THCA itself isn't classified as a controlled substance, creating what many consider a gray area. However, the DEA recently stepped in to clarify that THCA doesn't qualify as legal hemp because it can convert to delta-9 THC through decarboxylation.
State-by-State THC and THCA Regulations
Remember, state laws can vary significantly from federal regulations. Some states calculate legal hemp using "Total THC," which includes both THC and THCA, rather than just delta-9 THC. Florida uses a specific formula: Total THC = [delta-9 THC] + (0.877 × [THCA]). This means what's legal in one state might not be in another.
Labeling and Potency Concerns in THCA Products
Product labeling remains a significant concern. One study found that 44% of flower products had inaccurate THC content labels. Most mislabeled products actually overstated their THC potency. This highlights the importance of choosing reputable sources and understanding that label claims don't always match reality.
What Are the Key Differences Between THCA and THC?
Sometimes, seeing the facts side by side makes all the difference. Here's a quick reference guide that breaks down the essential characteristics of these two cannabinoids:
|
Characteristic
|
THCA
|
THC
|
|
Chemical Formula
|
C₂₂H₃₀O₄
|
C₂₁H₃₀O₂
|
|
Molecular Structure
|
Contains extra carboxyl group (-COOH)
|
Lacks carboxyl group
|
|
Psychoactive Effects
|
Non-intoxicating
|
Produces psychoactive effects
|
|
CB1 Receptor Binding
|
Cannot bind effectively
|
Binds directly to CB1 receptors
|
|
Primary Therapeutic Benefits
|
- Anti-inflammatory
- Neuroprotective
- Potential benefits for arthritis and IBD
|
- Pain relief (comparable to codeine)
- Appetite stimulation
- Nausea control
|
|
Consumption Methods
|
Raw cannabis, juicing, smoothies
|
Smoking, vaping, edibles
|
|
Heat Requirement
|
No heat required (raw form)
|
Requires heat (220°F-250°F) for activation
|
|
Legal Status
|
Federally legal in raw form (gray area)
|
Federally controlled substance
|
|
Conversion Rate
|
N/A
|
87.7% of THCA converts to THC when heated
|
|
Typical Consumption Amount
|
500-600mg (raw form) tolerable
|
10-25mg typical tolerance threshold
|
Remember, understanding these differences can help you make informed decisions about which compound might better support your wellness goals. The choice between THCA and THC often comes down to whether you want the therapeutic benefits with or without psychoactive effects.
Final Thoughts
The difference between THCA and THC goes far beyond that single letter — these cannabinoids represent two distinct paths for your wellness journey. THCA, with its extra carboxyl group, offers therapeutic support without any psychoactive effects, while THC brings its medical benefits alongside the well-known cannabis experience.
Heat makes all the difference. When you understand that decarboxylation transforms THCA into THC, you can choose your consumption method based on what you're hoping to achieve. Raw cannabis juicing lets you access THCA's benefits without intoxication, while smoking or vaping unlocks THC's full effects.
Both compounds show real therapeutic promise. THCA shines for its anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective qualities, potentially supporting those dealing with arthritis or neurodegenerative concerns. THC excels at pain relief that can match conventional medications, appetite support, and nausea control — especially valuable for cancer patients.
The legal landscape? It's complicated, and that's putting it mildly. THCA exists in a federal gray area until you heat it up, though recent DEA clarifications are trying to close that loophole. State regulations vary widely, so knowing your local laws matters.
Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to cannabis products. Whether you're seeking therapeutic benefits without intoxication or looking for the full spectrum of effects, understanding the THCA-THC relationship helps you make choices that align with your specific needs and goals.
Your wellness journey is uniquely yours, and these cannabinoids offer different tools to support your health. We invite you to explore what works best for you, always keeping safety and legality in mind as you make informed decisions about your well-being.
FAQ's About THCA VS THC
Q: How do the effects of THCA differ from THC?
A: THCA does not produce psychoactive effects like THC. While THC can make you feel relaxed and euphoric, THCA doesn't bind effectively to brain cannabinoid receptors, resulting in no intoxicating impact when consumed in its raw form.
Q: Is THCA legal in 2025?
A: The legal status of THCA varies by location. While it exists in a federal legal gray area as a hemp-derived product, it becomes a controlled substance when converted to THC through heating. State regulations differ, with some places allowing THCA under certain restrictions.
Q: Why do some cannabis retailers prefer selling THCA products?
A: Some retailers favor THCA products due to potentially lower tax burdens compared to traditional cannabis items. This can lead to better profit margins and allows for premium pricing strategies. However, regulations and market conditions can vary significantly by location.
Q: Can THCA naturally convert to THC over time?
A: Yes, THCA can slowly convert to THC through a natural process called decarboxylation. This occurs gradually when cannabis is exposed to heat, light, or oxygen over time. However, the conversion is much faster and more complete when cannabis is smoked, vaporized, or cooked.
Q: What are the main therapeutic benefits of THCA compared to THC?
A: THCA offers potential anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties without psychoactive effects. It may benefit conditions like arthritis and neurodegenerative disorders. THC, on the other hand, provides pain relief, appetite stimulation, and nausea control, but with accompanying psychoactive effects.
References
https://unitedrecoveryproject.com/rehab-blog/thca-vs-thc/
https://recovered.org/marijuana/thca/thca-vs-thc-and-other-cannabinoids
https://alignsonoma.com/thca-vs-thc/
https://www.rootsciences.com/blog/thca-vs-thc/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5549281/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tetrahydrocannabinolic_acid
https://www.cenikor.org/resources/thca-info/
https://arborswellness.com/blog/what-is-thca-how-is-it-different-from-thc/
https://www.webmd.com/mental-health/addiction/what-is-thca