What Does Inflammation Actually Feel Like?
Inflammation is a familiar term, often tossed around in discussions about health and wellness, but what does it actually entail? Fundamentally, inflammation is a natural process intricately tied to our immune system, serving as a vital response to bodily harm or illness.
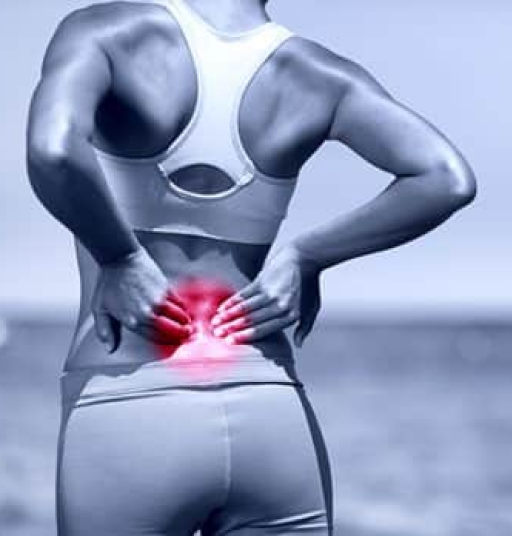
This process can manifest in various forms, ranging from a red, swollen ankle after a sprain to more subtle internal changes that aren't as easily noticed.
Understanding inflammation is key, as it plays a significant role in our body's defense mechanism. However, when this process goes awry, it can lead to discomfort and a host of health concerns. This article aims to shed light on the true nature of inflammation, exploring its characteristics, types, and the critical role it plays in our overall health and well-being.
What Is Inflammation?
Inflammation is the body's innate response to injury or infection, a signal that something is amiss. When an injury or infection occurs, various immune cells rush to the site, initiating the healing process. This response can be seen in two primary forms: acute and chronic inflammation.
Acute inflammation is the immediate, short-term reaction to an injury or illness, characterized by redness, warmth, swelling, and sometimes pain. It's a protective mechanism that aims to remove harmful stimuli and initiate the healing process.
On the other hand, chronic inflammation is a longer-term response, often occurring when this protective mechanism lingers and turns against the body's own tissues. It can be less noticeable but is linked to a range of health conditions, from joint pain to more complex autoimmune diseases.
Understanding these two types is key to comprehending how our bodies react to different stressors and injuries.
The Immune System and Inflammation: What's the Link?
The immune system, our body's sophisticated defense network, plays a pivotal role in managing inflammation. At the heart of this system are white blood cells and immune cells, which act as guardians against foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses.
When these cells detect a threat, they trigger an inflammatory response to protect the body and facilitate healing. This response is marked by the release of cytokines, signaling proteins that guide immune cells to the infection or injury site.
But, the immune system can sometimes misinterpret its targets, leading to autoimmune diseases. In these cases, the body's defense mechanism mistakenly attacks its own tissues, causing chronic inflammation. This can result in a range of symptoms, from skin rashes and digestive issues to joint pain and bloating.
The complexity of the immune response in inflammation underscores the importance of maintaining a balanced and healthy immune system. By keeping our immune system in check, we can better manage and understand the inflammatory processes, ultimately leading to improved health and wellness.
What Does Inflammation Feel Like?
Inflammation is a physical sensation that can vary greatly depending on its cause and location in the body.
Commonly, it presents as a feeling of warmth or heat in the affected area, often accompanied by redness. This is due to increased blood flow as the body rushes nutrients and immune cells to tackle the issue. In some cases, inflammation can also cause discomfort or tenderness, making the area sensitive to touch or movement.
Swelling is another hallmark of inflammation. It's the result of fluid accumulation as the body's way of protecting and healing the affected area.
In cases of internal inflammation, such as within the digestive system, you might experience symptoms like bloating or abdominal pain. However, not all inflammation is palpable or visible. Chronic inflammation, in particular, might manifest subtly, potentially leading to fatigue or even mood changes.
Understanding these sensations is key, as they are the body's way of signaling that it's undergoing a healing process or fighting against something that's not quite right.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Inflammation?
Inflammation can manifest in various signs and symptoms that signal your body is responding to an injury or stressor.
These include:
-
Joint Discomfort: A common symptom, especially noticeable in cases of chronic inflammation.
-
Rashes: These can appear as a skin response, indicating inflammation under the surface.
-
Bloating: Often a sign of internal inflammation, particularly in the digestive system.
-
Skin Conditions: Various skin issues can be indicative of underlying inflammatory responses.
-
Redness and Warmth: Frequently accompanying inflammation, these are signs of increased blood flow to the affected area.
Recognizing these symptoms is the first step in understanding how your body reacts to different types of stress and injury and can be helpful in addressing any underlying issues.
What Can Cause Inflammation?
While inflammation is a natural response of the body, various factors can trigger or exacerbate this process. Understanding these causes can help in managing and potentially reducing the occurrence of inflammation.
Autoimmune Conditions
Autoimmune conditions are scenarios where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own cells, mistaking them for foreign invaders. This misdirected immune response can lead to a state of chronic inflammation as the body continuously tries to heal from the perceived threat.
In these cases, the inflammation isn't a response to an external injury but rather an internal error in the immune system's functioning. Managing these conditions often involves strategies to modulate the immune response and reduce its overactivity.
Heart Health
The link between long-term inflammation and heart health is significant. Chronic inflammation has been associated with a range of cardiovascular issues, including heart disease and type 2 diabetes. This type of inflammation can contribute to plaque buildup in blood vessels, a key factor in heart diseases.
It's not just about the presence of inflammation but also its duration and intensity that can impact heart health. Managing inflammation, therefore, becomes crucial in maintaining cardiovascular health and preventing long-term complications.
Diet
Diet plays a pivotal role in influencing inflammation. Certain foods and nutrients can trigger an inflammatory response, while others can help reduce it.
Foods high in sugars and saturated fats are known to contribute to increased inflammation, as do processed foods. On the other hand, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help manage inflammation.
Individual sensitivities and intolerances also play a role. What might cause inflammation in one person may not have the same effect in another.
Understanding these dietary impacts is crucial, as it offers a practical way to manage inflammation through daily choices. Paying attention to how your body reacts to different foods can be a key strategy in controlling and understanding inflammation.
Hydration
Hydration plays a more significant role in our body's inflammatory response than we might realize. Dehydration can lead to a heightened state of inflammation.
When the body doesn't receive adequate water, it may struggle to eliminate toxins and waste materials, potentially leading to an inflammatory response. Proper hydration helps in maintaining cellular health and ensuring efficient functioning of the body's systems, including the immune system.
Dehydration can also exacerbate issues like constipation, which in turn can cause uncomfortable inflammation and bloating. Staying well-hydrated is not just about quenching thirst but also about keeping inflammation and related digestive discomforts at bay.
Stress Levels
Stress is more than just a mental or emotional burden — it has tangible physical effects, including the potential to increase inflammation. The body's stress response, characterized by the release of cortisol and other stress hormones, can trigger an inflammatory response.
Chronic stress, in particular, can lead to a prolonged state of inflammation, impacting overall health. Managing stress through techniques like mindfulness, adequate rest, and physical activity can be a key part of controlling inflammation.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as exposure to pollutants or allergens, can also contribute to inflammation. These external irritants can trigger the immune system, leading to an inflammatory response.
In some cases, prolonged exposure to poor air quality or certain chemicals can lead to chronic inflammation. Being aware of one’s environment and minimizing exposure to potential irritants can help in managing inflammation levels.
How Is Inflammation Diagnosed?
When it comes to diagnosing inflammation, healthcare providers take a comprehensive approach.
Initially, they may engage in a detailed conversation with you to understand your symptoms and any relevant personal or family health history. This dialogue is key for identifying potential causes of inflammation. Following this, physical examinations are often conducted to observe any visible signs of inflammation like redness or swelling.
Your provider may also order blood tests. These tests can measure markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP), which is often elevated in cases of inflammation. Other blood markers might include elevated white blood cell count, signaling an ongoing immune response.
Through these steps, healthcare professionals aim not just to identify inflammation but to understand its underlying cause, which is essential for effective management and treatment.
Can You Take Medicine for Inflammation?
For managing inflammation, medications such as NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), including ibuprofen and naproxen, are commonly used. These drugs work by reducing the production of substances in the body that cause inflammation. Corticosteroids are another class of medication used for their potent anti-inflammatory effects.
However, these medications can come with side effects and risks, especially with long-term use. Side effects might include stomach irritation, increased risk of heart problems, and others. Due to these potential risks, many people are turning towards more natural approaches and lifestyle changes to manage inflammation. These alternatives aim to support the body's natural healing processes without the drawbacks associated with over-the-counter medications.
As always, it’s critical to talk to your doctor before adding any new medications or supplements to your routine.
What Lifestyle Changes Can Help Support the Body's Inflammatory Response ?
Adopting certain lifestyle changes can significantly support your body's inflammatory response, helping to manage and potentially reduce inflammation.
Eating Anti-inflammatory Foods
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing inflammation. Including anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric, known for its curcumin content, can help.
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet like the Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, is also known for its anti-inflammatory benefits. Conversely, reducing your intake of processed foods and carbohydrates that can trigger inflammation is often recommended.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can lead to prolonged inflammation. Engaging in stress-reduction practices like mindfulness, meditation, or even simple breathing exercises can be helpful. Adequate sleep and relaxation techniques also play a significant role in managing stress levels.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is known to improve overall health and can help reduce inflammation. Activities like running, swimming, or yoga can be particularly helpful, offering both physical and mental health benefits.
Understanding and Identifying Triggers
Being aware of what triggers your inflammatory response is key. This could be certain foods, environmental factors, or stressors. Keeping a journal to track your symptoms and potential triggers can be a helpful tool.
The Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups are essential, especially for recognizing early signs of chronic inflammation. These check-ups can help in monitoring your health and ensuring any signs of prolonged inflammation are addressed promptly.
Incorporating these lifestyle changes can support your body's natural ability to manage inflammation, contributing to overall health and well-being. Remember, each person's body is different, so it's important to find what works best for you.
The Bottom Line
Understanding and effectively managing inflammation is an important aspect of maintaining overall health. Embracing a holistic approach to health, which includes nurturing the body and mind, is also essential.
To learn more about how to support your wellness, visit the Muscle MX blog.
Sources:
Inflammation: What Is It, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment | Cleveland Clinic
The Immune System | Johns Hopkins Medicine
Dehydration - Symptoms & causes | Mayo Clinic
Foods that fight inflammation | Harvard Health