Does Mental Health Impact Physical Health?
In recent years, the link between mental and physical health has gained significant attention. Although many used to think of the mind & body as separate entities, ongoing research has shown that they are intricately connected. How we feel mentally often manifests physically, and vice versa. The relationship between mental and physical health is complex, affecting everything from immune function to overall well-being.
Whether it’s chronic stress leading to high blood pressure, depression causing fatigue, or anxiety resulting in headaches, the impacts are undeniable. That’s why we will be exploring the many ways mental health affects physical health and how improving one can benefit the other.
What is Mental Health?
Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It influences how we think, feel, and behave, as well as how we handle stress, relate to others, and make decisions. Mental health is more than the absence of mental illness—it is an integral part of overall health that affects quality of life, relationships, and work performance.
How It’s Diagnosed
Mental health disorders are diagnosed through a combination of clinical evaluation, patient history, and standardized psychological assessments. Diagnosis often begins with a primary care physician or mental health professional assessing symptoms like mood, behavior, and thought patterns. For example, someone experiencing prolonged sadness, fatigue, or lack of interest in activities may be evaluated for depression. Anxiety, on the other hand, might be diagnosed based on symptoms like constant worry, racing thoughts, and physical signs such as a rapid heartbeat or sweating.
Mental health diagnoses also take into account the duration and intensity of symptoms, along with their impact on daily functioning. Specialists use tools like the DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders) to classify and diagnose conditions such as anxiety, depression, bipolar disorder, and more.
How It’s Typically Treated
Mental health treatment varies depending on the condition but often includes a combination of therapy, medication, lifestyle changes, and sometimes alternative treatments like CBD products. For instance, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is one of the most widely used forms of therapy, helping individuals reframe negative thought patterns. Medications such as antidepressants, anti-anxiety drugs, and mood stabilizers may be prescribed to manage symptoms.
For those looking for a more natural approach, products like CBD gummies have gained popularity for managing stress, anxiety, and promoting better sleep. Cannabinol (CBD) in general known for its blissful effects and has become a supplemental tool for individuals looking to enhance their mental wellness routines.
What is Physical Health?
Physical health refers to the well-being of the body and its ability to function optimally. It includes everything from maintaining a healthy weight and cardiovascular health to flexibility, strength, and stamina. Physical health impacts longevity, energy levels, and resilience against disease.
What are Some Ways a Person's Physical Health Can Decrease?
A person's physical health can decline due to a variety of factors, often interrelated and multifaceted. Understanding these factors can help in taking proactive steps to maintain and improve overall well-being. Here are some key ways physical health can decrease:
-
Poor Nutrition: Consuming excessive amounts of processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats while lacking essential nutrients can lead to obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and other chronic conditions. Also, insufficient intake of vitamins and minerals (e.g., Vitamin D, calcium, iron) can cause issues like anemia, weakened bones, and compromised immune function.
-
Physical Inactivity: Lack of regular exercise can result in muscle atrophy, reduced cardiovascular health, increased body fat, and higher risk of chronic diseases such as hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Over time, inactivity can even lead to decreased flexibility and joint problems, making daily activities more challenging.
-
Substance Abuse: Certain substances can of course, impact one’s physical health, such as:
-
Smoking: Increases the risk of lung cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), heart disease, and stroke.
-
Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Can lead to liver disease, pancreatitis, cardiovascular problems, and impaired cognitive function.
-
Illicit Drugs: Use of drugs like cocaine, heroin, and methamphetamine can cause severe organ damage, mental health issues, and increased risk of infectious diseases.
-
Lack of Sleep: Chronic lack of sleep can weaken the immune system, impair cognitive functions, increase the risk of accidents, and contribute to conditions like obesity and heart disease. Conditions such as insomnia, sleep apnea, and restless legs syndrome can disrupt restful sleep and negatively impact overall health.
-
Exposure to Environmental Toxins: Air and water pollution can cause respiratory issues, cardiovascular problems, and increase the risk of certain cancers. Contact with hazardous chemicals in workplaces or through consumer products can lead to acute and chronic health issues, including skin conditions and neurological damage.
-
Poor Hygiene: Inadequate personal hygiene can facilitate the spread of infectious diseases like the flu, common cold, and gastrointestinal infections. Poor hygiene can lead to skin infections, acne, and other dermatological issues.
-
Neglecting Preventive Healthcare: Missing regular health check-ups and screenings can delay the diagnosis and treatment of diseases such as cancer, hypertension, and diabetes. Not staying up-to-date with vaccinations increases vulnerability to preventable diseases.
-
Injuries and Accidents: Accidents can result in broken bones, concussions, and other injuries that may have long-term health implications. Injuries that heal improperly can lead to persistent pain and mobility issues.
-
Genetic and Hereditary Factors: Genetics can predispose individuals to conditions like cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and certain cancers, affecting their physical health. A family history of diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, or hypertension can increase an individual's risk.
-
Aging: As people age, they may experience a decline in muscle mass, bone density, and organ function, increasing susceptibility to various health issues. Older adults are more likely to develop chronic diseases like arthritis, osteoporosis, and cardiovascular diseases.
-
Infectious Disease: Diseases like the flu, COVID-19, and other viral or bacterial infections can temporarily or permanently impact physical health. Also, conditions such as HIV/AIDS or hepatitis can have long-term effects on health and immune function.
-
Overexertion and Physical Strain: Excessive physical activity without adequate rest can cause repetitive stress injuries, such as tendinitis or stress fractures. Chronic overexertion can lead to exhaustion, weakened immune response, and increased vulnerability to illnesses.
-
Poor Social Determinants of Health: Limited access to healthcare, nutritious food, and safe living conditions can negatively impact physical health. Lack of knowledge about healthy lifestyle choices can also contribute to poor health outcomes.
How Does Someone Stay Physically Healthy?
Maintaining physical health involves the following:
-
Exercise: Regular physical activity strengthens the heart, improves circulation, and helps regulate body weight. It also promotes the release of endorphins, chemicals that improve mood and reduce stress.
-
Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains supports bodily functions, boosts the immune system, and prevents chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease.
-
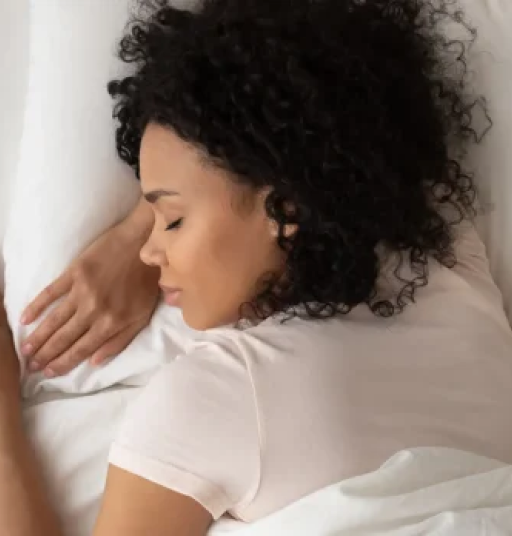
Sleep: Adequate sleep is vital for physical recovery, cognitive function, and emotional regulation. Lack of sleep has been linked to weakened immunity, poor concentration, and increased stress.
-
Medical Care: Regular check-ups, vaccinations, and screenings for conditions like high blood pressure or cholesterol help prevent and manage potential health issues.
Ways That Mental Health Impacts Physical Health
The connection between mental and physical health is well-established, with mental well-being playing a significant role in overall physical health. Below are key ways that mental health can impact physical well-being:
-
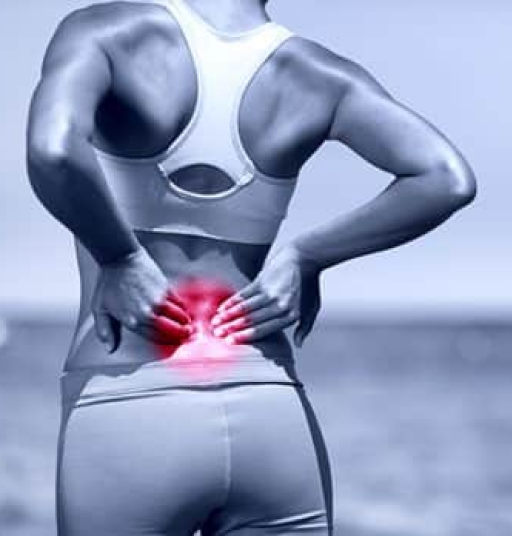
Stress and the Body: Again, chronic stress is one of the most common mental health issues impacting physical health. When a person experiences stress, their body releases cortisol, a hormone that prepares the body to handle challenging situations. While occasional stress can be beneficial, chronic stress leads to prolonged cortisol exposure, which can have negative effects like high blood pressure, a weakened immune system, and weight gain. Over time, this may lead to heart disease, diabetes, and other serious conditions.
-
Depression and Physical Symptoms: Depression doesn’t just affect mood—it often causes physical symptoms. People with depression may experience chronic fatigue, muscle aches, headaches, and digestive issues. The lack of motivation and energy can make it difficult to engage in healthy behaviors, such as exercising or maintaining a balanced diet, which further exacerbates physical health problems.
-
Anxiety and Its Physical Effects: Anxiety can manifest in various physical symptoms, including a rapid heart rate, shortness of breath, dizziness, and digestive issues like nausea or stomach pain. These physical manifestations of anxiety are caused by the body’s fight-or-flight response being triggered too often. When this happens repeatedly, it can take a toll on the cardiovascular system, leading to higher risks of heart attacks and strokes.
-
Impact of Mental Health on Immune Function: There is a strong link between mental health and the immune system. Chronic stress, anxiety, and depression can weaken immune function, making the body more susceptible to infections and illness. Conversely, good mental health strengthens the immune system, helping the body fight off diseases more effectively. This connection highlights the importance of managing mental health to maintain a strong and resilient immune system.
-
Mental Health and Sleep Quality: Mental health disorders like depression and anxiety are closely linked to sleep problems. Insomnia and other sleep disorders are common among individuals struggling with mental health issues, leading to fatigue, weakened immunity, and an increased risk of chronic diseases. Conversely, improving sleep quality through relaxation techniques, physical activity, or using calming products like CBD gummies can enhance both mental and physical health.
-
Substance Abuse and Physical Health: Mental health struggles often lead individuals to turn to unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as substance abuse. This can involve alcohol, drugs, or even overuse of prescription medications. Substance abuse not only worsens mental health conditions but also causes significant damage to physical health, leading to liver disease, heart problems, and an increased risk of accidents and injuries.
-
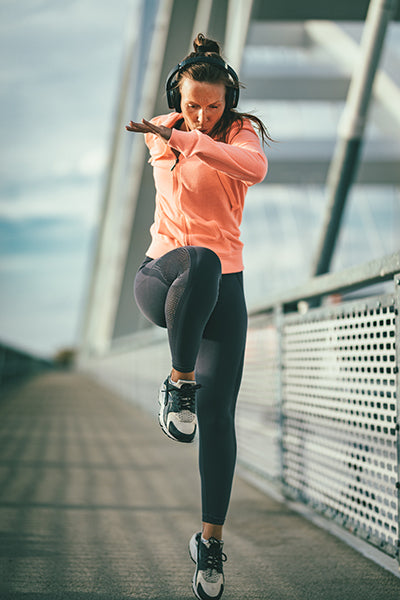
Exercise as a Link Between Mental and Physical Health: Exercise is one of the most effective ways to improve both mental and physical health. Physical activity releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters. It also reduces the production of cortisol, helping to manage stress. Additionally, exercise has been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, while also improving cardiovascular health, muscle strength, and overall energy levels. Finding activities that you enjoy, whether it’s yoga, running, or swimming, can have a profound impact on both mental and physical well-being.
-
Diet and Mental Health: The food we eat doesn’t just impact our physical health—it also affects our mental health. Diets high in sugar, processed foods, and unhealthy fats have been linked to increased rates of depression and anxiety. On the other hand, diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins support both brain and body function. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish like salmon and in supplements, are particularly important for brain health, helping to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
-
Chronic Illness and Mental Health: People with chronic physical illnesses are more likely to experience mental health challenges. Conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and cancer often bring with them a high level of stress, anxiety, and depression. Managing these illnesses requires not just physical care but also mental health support to improve overall quality of life. In some cases, integrating certain CBD products may provide additional potential benefits, thus helping to manage stress and improve sleep for individuals dealing with chronic conditions.
How Our Understanding of Mental Health Has Grown and Its Future
As research into mental health and its effects on physical health grows, so does our understanding of the interconnectedness of the mind and body. In the past, mental health was often overlooked or considered less important than physical health. Presently, we know that mental well-being is integral to overall health and that treating mental health issues can improve physical outcomes.
Looking to the future, the hope is that mental health will continue to be destigmatized, with more people seeking care and understanding the importance of addressing mental well-being. Advances in treatments, including therapies, medications, and wellness products, provide individuals with more tools than ever to manage their mental and physical health. By focusing on holistic care, we can continue to improve the lives of individuals and communities as a whole.