Throbbing Pain Explained: What Is Throbbing Pain?
|
| Pain is an essential part of our survival mechanism. But, when it becomes chronic, it can rob us of our vitality and disrupt our quality of life. |
Today, we'll explore throbbing pain, its characteristics, and common causes, including toothache, migraine headaches, and neuralgia. We'll also delve into the critical subject of pain management, discussing over-the-counter medications and their potential side effects and the importance of seeking medical advice.
What Is Throbbing Pain?
Pain, in all its forms, has shaped our evolution and influenced our behavior and decision-making. Throbbing pain is one such type with a unique and distinct quality that sets it apart from other forms of pain, such as aching pain or sharp pain.
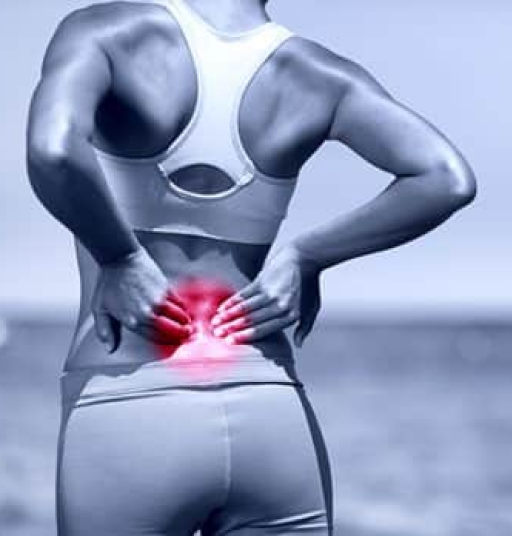
Throbbing pain is a type of pain that is characterized by a rhythmic beating or pulsing sensation. It is often described as a deep, dull ache that is felt in the affected area. The cause of throbbing pain can be a variety of factors, such as an injury, an infection, or an underlying medical condition. For example, a headache can cause throbbing pain in the head, while toothaches can cause throbbing pain in the jaw and mouth.
In many ways, throbbing pain reminds our bodies that something needs to be addressed. It is a way for our bodies to communicate to us that an issue needs to be resolved — our throbbing pain reminds us that we need to take action to identify and address the underlying cause.
However, not all throbbing pain signals the presence of a health condition; the causes of throbbing pain can vary, and not all of the causes are severe or dire. In some cases, throbbing pain is simply a sign of stress or an emotional response to a particularly stressful or unpleasant situation.
Let's look at some of the more common causes of throbbing pain.
What Are Common Causes of Throbbing Pain?
Throbbing pain can be caused by a wide variety of factors, and identifying the cause of your discomfort is a key step toward finding the right treatment path.
Toothaches
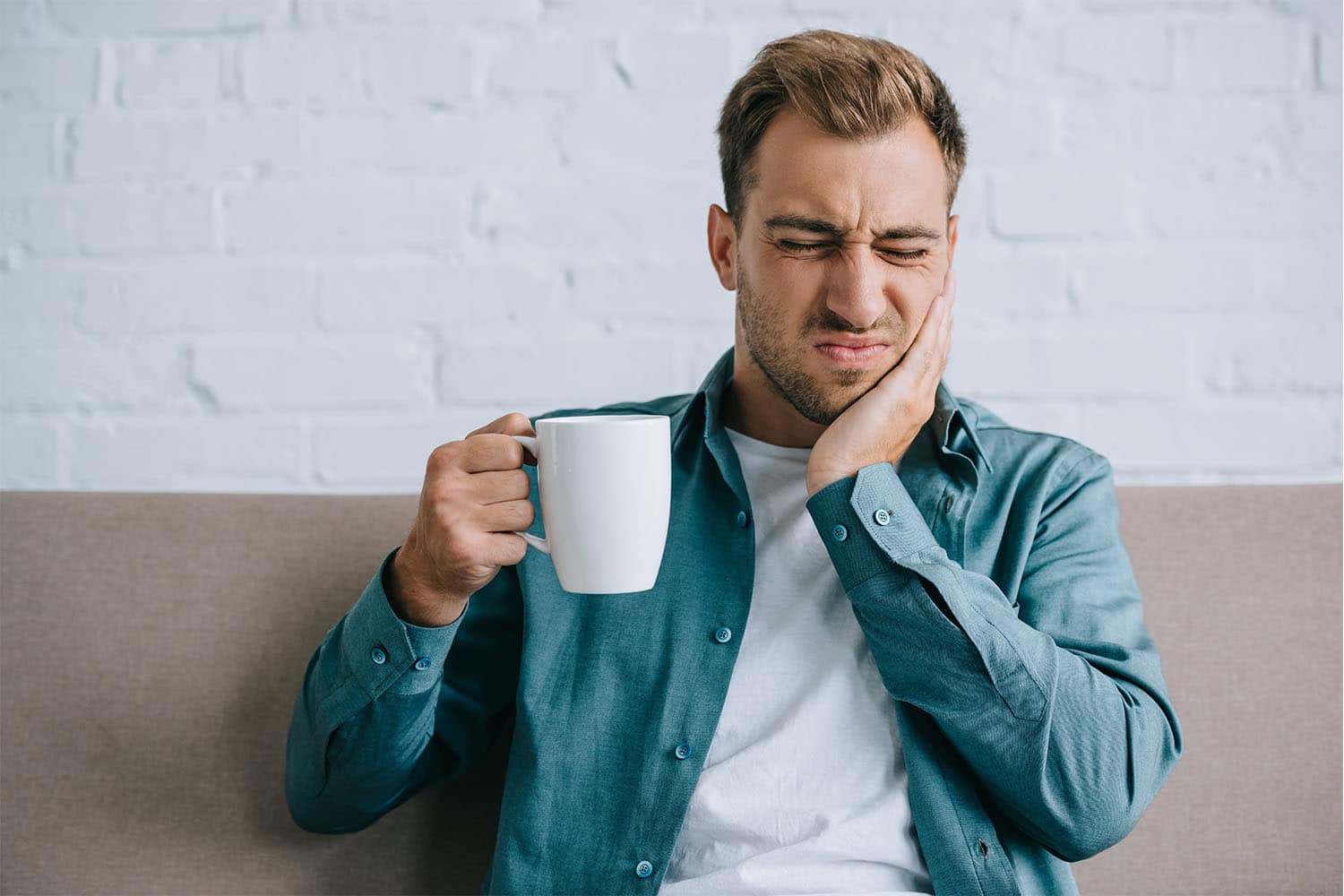
Have you ever experienced a toothache so intense that it felt like someone dropping an anvil on your jaw? Unfortunately, this is the hallmark symptom of a toothache — a story that's all too familiar for many of us.
But what exactly causes the physical sensation of a toothache? It could be something as simple as a cavity or as complex as gum disease or an impacted tooth. Regardless of the source, the effects of a toothache can be far-reaching, making it difficult to eat, sleep, and even speak.
The good news is that toothache is a story with a happy ending. Many treatments are available, from antibiotics to pain relievers to dental surgery. The key is to find the proper treatment for the severity of the problem.
Migraine Headaches
Migraines are a type of headache that can cause intense, pulsing pain. They're like a drummer in your head, pounding away relentlessly. But what causes migraines? They can be triggered by various factors, from stress to hormone fluctuations to chemical imbalances in the brain.
Migraines are a story that's all too common, affecting at least 10% of the population. And the tale is often a female one, with the peak age of onset being between 20 and 45. But the good news is that there are treatments available for migraines. These can include medications, lifestyle changes, and stress reduction therapies designed to soothe the throbbing pain.
Neuralgia
When it comes to the complex world of throbbing pain, neuralgia is one of the most mysterious and challenging to understand. This pain arises from irritation or injury to a nerve, creating a fiery burning sensation that spreads to different parts of the body.
In addition, the pain can be sudden and intense, making it difficult to pinpoint the source — but behind this perplexing discomfort lies a deep biological process involving the intricate interplay of neurotransmitters and pain.
Every time we feel pain, our nervous system sends a signal to the brain, alerting it to the source of the discomfort. This signal is transmitted by neurotransmitters, chemical messengers that travel along the nerves, transmitting information from one neuron to another. In the case of neuralgia, these neurotransmitters are firing excessively, creating a chronic and intense pain experience.
How Can You Treat Throbbing Pain?
As we delve into the world of throbbing pain management, it's important to remember that everyone's journey is unique. But one thing we can all agree on is that when it comes to pain, we want relief, and we want it fast. So, let's explore the options available, starting with the over-the-counter medications that can offer a quick and convenient solution.
OTC Medications
Think about the last time you had a headache that wouldn't go away. Did you reach for a bottle of ibuprofen or aspirin?
These are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs, and they're some of the most popular over-the-counter options for throbbing pain relief. However, as with any medication, there can be side effects, so it's always a good idea to be informed before you pop a pill.
Turning to the Professionals
Sometimes, the source of throbbing pain can be too deep, too complicated, or just downright mysterious. That's when it's time to turn to the professionals. Imagine you've been experiencing chronic pain for weeks or even months.
You've tried everything in your OTC arsenal, but nothing seems to work. That's when it's time to seek expert help. Your doctor will evaluate your health conditions, including any underlying causes of your pain, and recommend the best treatment options.
Biopsychosocial Techniques
Pain can be more than just physical — it can also manifest as psychological and emotional distress, making it difficult to manage with traditional medical treatments. Fortunately, there are mind-body techniques that can help reduce the intensity of throbbing pain.
These biopsychosocial techniques include relaxation and breathing exercises, cognitive behavioral therapy, and mindfulness. These approaches can help to reduce stress and improve the body's ability to cope with pain.
Pain as a discipline has come a long way. In the past couple of decades, researchers and scientists have learned that there is much more to pain than meets the eye and that the emotional and psychological components play an integral role in how we perceive it.
Holistic Approaches to Pain Relief
As discussed, pain cements itself into thoughts, behaviors, and emotions, and to truly understand the experience of throbbing pain, we must take a holistic approach. For example, think of a time when you experienced throbbing pain. What emotions did you feel? How did your thoughts affect your behavior in response to the discomfort? For example, did you find yourself avoiding certain activities or seeking out distractions from the pain?
We tend to avoid it when we're in pain, but this only perpetuates the cycle. When we experience an injury during acute recovery, we need to focus on the process of healing. But even after the healing completes, we may find ourselves falling into an avoidance pattern, trying to avoid activities or experiences that might trigger the pain.
During our recovery process, we train our bodies and minds to fear pain, perpetuating the cycle. To break the cycle of throbbing pain, we must learn to face our fears and confront the pain head-on.
That's why breathing and relaxation exercises can be so helpful in managing pain. They allow us to focus on the present moment and manage our emotions and physical sensations rather than avoiding them. These mindfulness techniques can also be combined with cognitive behavioral therapy, helping us to identify and challenge the thoughts that may lead us to fear pain.
Does Throbbing Occur in Rhythm With Your Heartbeat?
Conventional wisdom tells us that throbbing pain is often associated with the heartbeat's rhythm and that pain's throbbing quality is a direct result of our body's arterial pulsations. But research suggests that this widely held belief is, in fact, a myth.
At the University of Florida in 2012, researchers tested this assumption by studying the connection between the subjective experience of throbbing pain and the actual pulsation of our blood vessels.
To their surprise, they found that the throbbing rate was much slower than the arterial pulse, and the two rhythms exhibited no correlation. This led the researchers to conclude that the throbbing quality of pain is not a primary sensation but rather an emergent perception within the central nervous system.
So why does this matter? By understanding the true nature of pain's pulse, we can better measure and treat severe and debilitating pain. This is an important step forward in the world of pain management and a revelation that pain is primarily neurological in origin.
This is a good sign, as it suggests that we can better target and manage throbbing pain through a combination of psychological, physical, and pharmacological approaches.
Conclusion
Throbbing pain can be caused by a wide variety of factors, and there are various treatment options available. From OTC medications to physical therapy and relaxation techniques, finding the right treatment method for your needs may take some trial and error.
Our mission at Muscle MX is to empower individuals with the necessary knowledge to enhance their body's performance, reduce discomfort, and pave the way for a healthier, more active lifestyle.
Sources:
Is There a Relationship between Throbbing Pain and Arterial Pulsations? | National Library of Medicine
What Is Migraine? | Headache | JAMA Network
Breathing Exercise for Relaxation | Children's Hospital of Pennsylvania